3.6It is the second byte transmitted in each communication information frame. The function codes that can be defined in the ModBus communication protocol are 1 to 127. As a host request, the function code tells the slave what action to perform. As a slave response, the function code returned by the slave is the same as the function code sent from the host, and indicates that the slave has responded to the host and has performed related operations.1.3 Data area:
The data area includes what information needs to be returned by the slave or what action needs to be performed. This information can be data (such as: switch input/output, analog input/output, register, etc.), reference address, etc. For example, the host tells the slave to return the value of the register (including the starting address of the register to be read and the length of the register to be read) through function code 03, and the returned data includes the data length and data content of the register. For different slaves, the address and data information are different (a communication information table should be given).
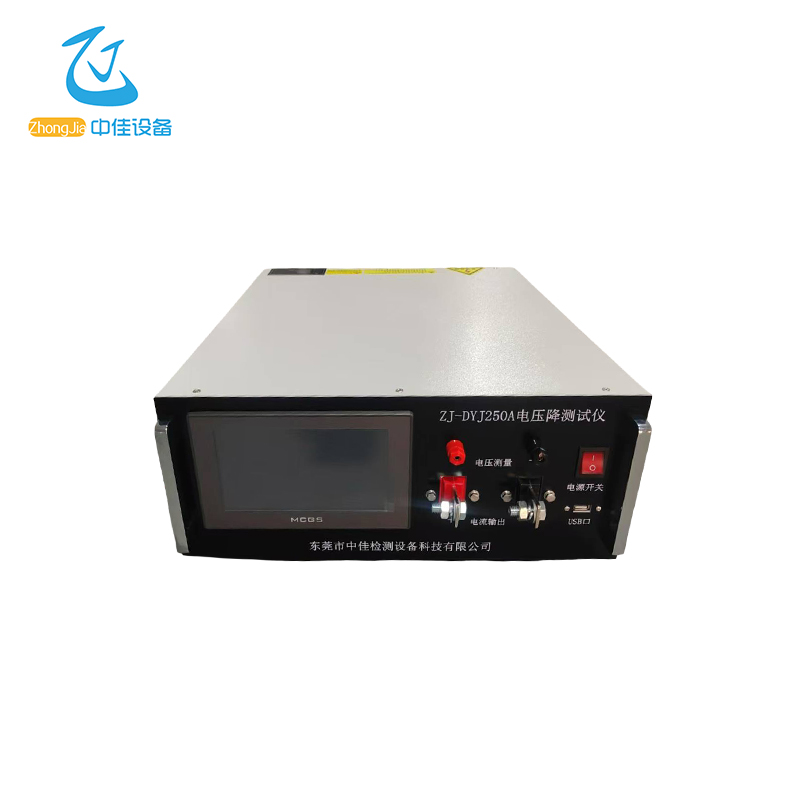
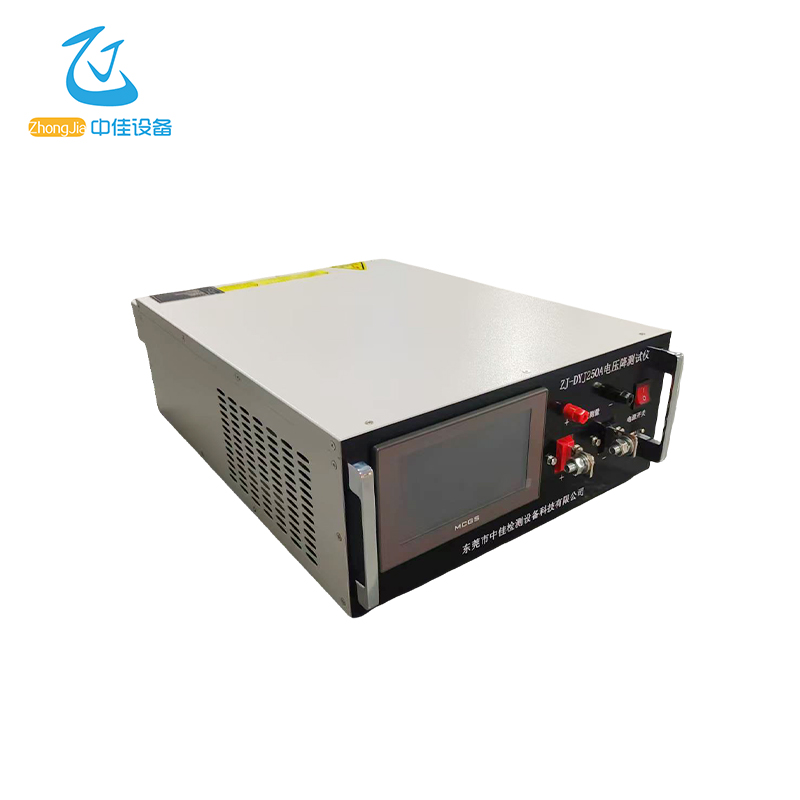
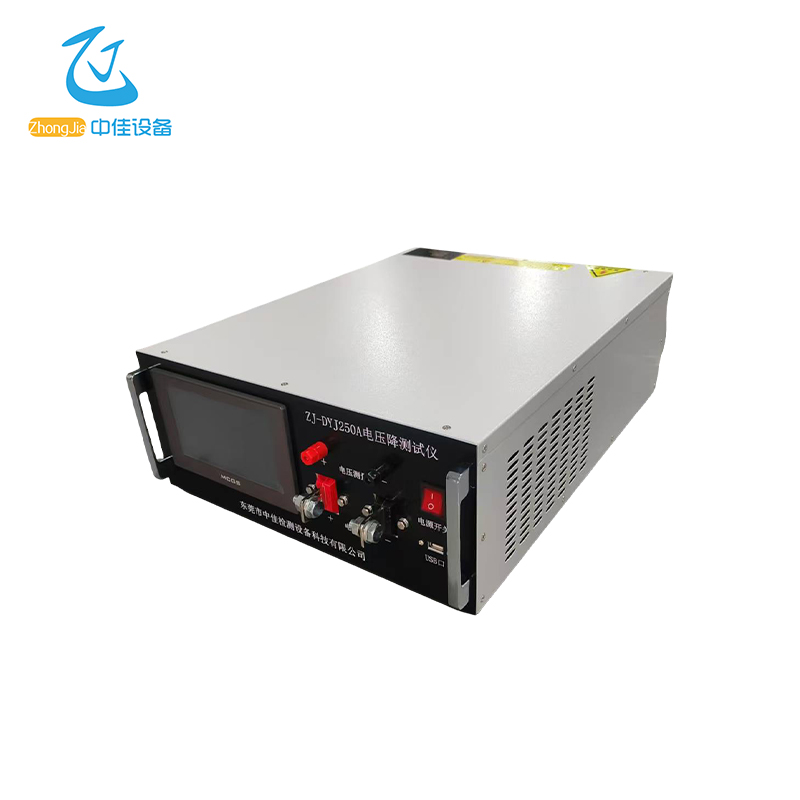
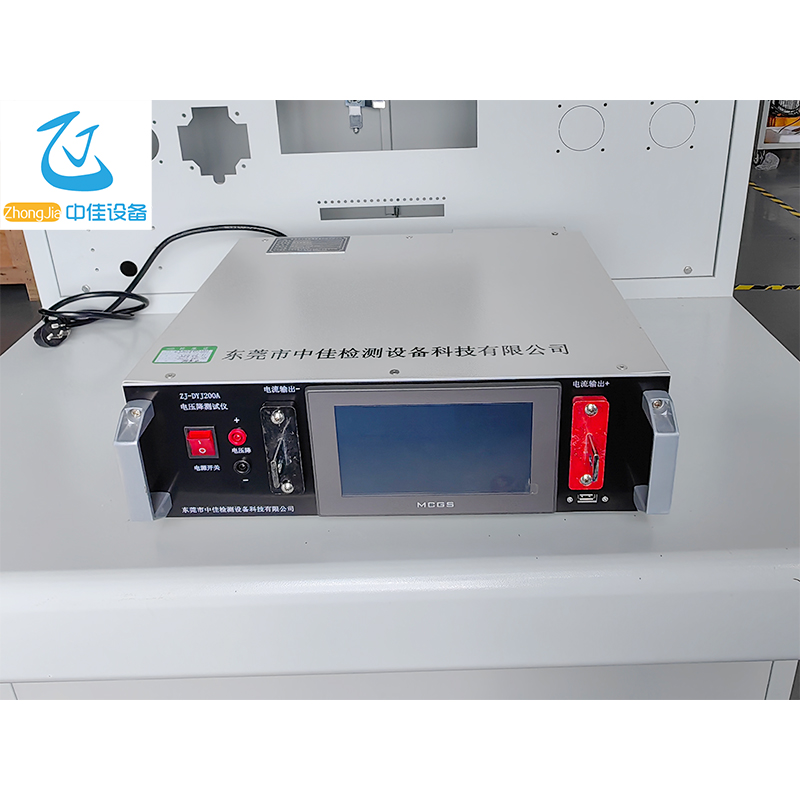
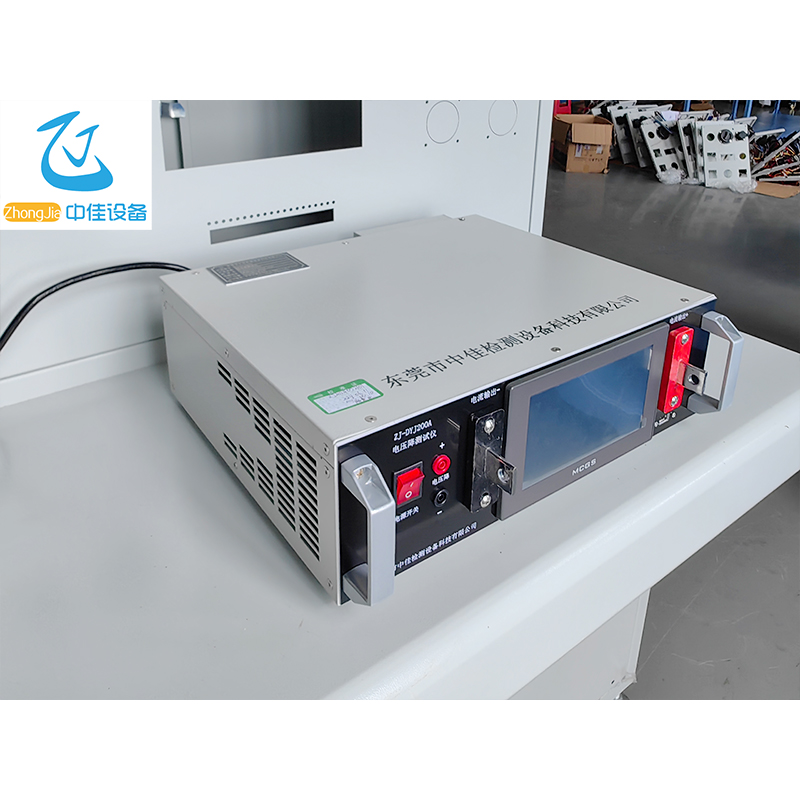
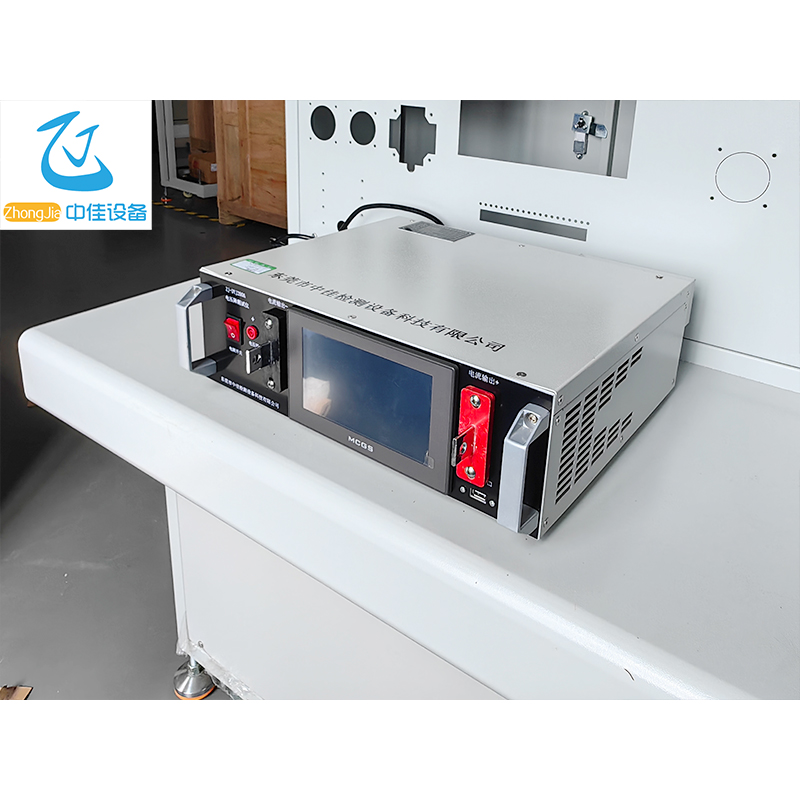
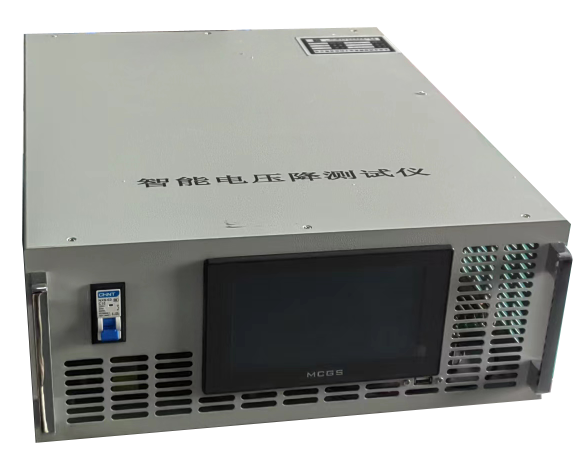
The power supply adopts the Modbus communication protocol. The host (PLC, RTU, PC, DCS, etc.) can read its data register arbitrarily using the communication command (function code 03) (the data information table is detailed in the appendix).
The response command format is the slave address, function code, data area and CRC code. The data in the data area are all two bytes, and the high bit is in front.
4. Static time requirements
Before sending data, the data bus static time, that is, the time when no data is sent, is required to be greater than (5ms when the baud rate is 9600).